Metal sulfides are highly active photocatalysts for water reduction to form H2 under visible light irradiation, whereas they are unfavorable for water oxidation to form O2 because of severe self-photooxidation (i.e. photocorrosion). Construction of a Z-scheme system is a useful strategy to split water into H2 and O2 using such photocorrosive metal sulfides because the photogenerated holes in metal sulfides are efficiently transported away. In this work, we demonstrate powdered Z-schematic water splitting under visible light and simulated sunlight irradiation by combining metal sulfides as an H2-evolving photocatalyst, reduced graphene oxide (RGO) as an electron mediator, and a visible-light-driven BiVO4 as an O2-evolving photocatalyst. This Z-schematic photocatalyst composite is also active in CO2 reduction using water as the sole electron donor under visible light.
Read full article here: JACS, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b05304
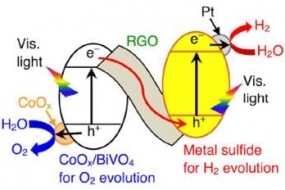
Illustration of z-scheme systems Consisting of Metal Sulfides, CoOx-loaded BiVO4, and a Reduced Graphene Oxide Electron Mediator